Two way Radio Technology Explained
Line of Sight
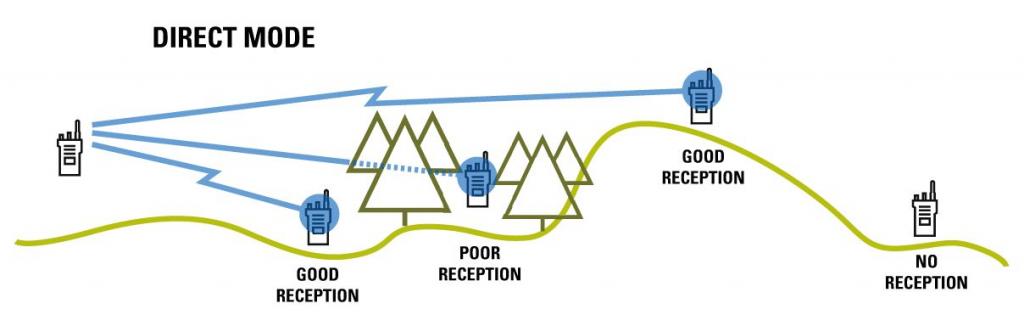
Effective radio transmission requires a clear path between the receiving and transmitting antennas. That free path is the line of sight.
There are 3 types of line of sight based on your topographical environment.
- Clear Line of Sight – This is when you achieve optimal signal abilities with your two way radio. In this case, there are no visual obstructions, and the Fresnel effect is not impacted at all, allowing clear receiving and transmitting.
- Near Line of Sight – Some obstructions of signaling which doesn’t greatly impact signal, but can result in errors or trouble with the throughput of messaging etc. The Fresnel zone would be slightly obstructed by say a tree, or the top of a hill.
- Non-Line of Sight – In this case, obstructions such as hills and other buildings etc. prevent the best use of signal abilities and the Fresnel zone is impacted. This doesn’t necessarily mean that signals cannot work, but rather they do not work all the time – depending on the situation (storms, cloud cover etc.)
How will a radio talk?
This is one of the most common questions people ask when renting or buying a two-way radio. Unfortunately there isn’t a quick answer as a number of factors come in to play.
- Line of Sight – Frequencies used in two way radios travel in a straight lines (line-of-sight), and generally cannot travel beyond the horizon. So the distance to the horizon is the maximum communication range for these two way radios, without the aide of additional equipment such as a repeater BUT many other factors can diminish the range.
- Topographical interference – Radios signals are sometimes blocked by solid objects, natural and man made, examples Metal, concrete and Hills – If you live in an area with hills, they are like metal, no radio signal will pass through them. to name a few. Radio waves will travel through some non-metallic objects such as drywall, human bodies, furniture, and many other objects. BUT The denser an object, the more it reduces the signal strength. So with each successive object a signal passes through, it’s range is shortened.
- Elevation – One of the easiest ways to increase your range is to increase your height – increasing your line of sight. If you are near the edge of your range and experiencing a weak signal try getting to a higher location. Walk up a hill or use something to make yourself taller. Remember, just a foot or two can make a big difference in range.
- Battery Life – Make sure your battery is fully charged. Radio signals weaken when their battery is low.
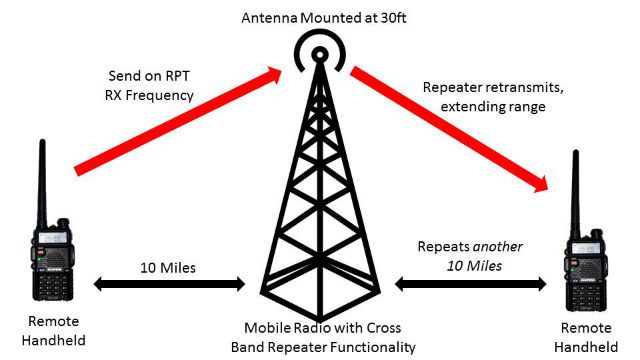
- Repeater System – A repeater is used to boosts signal, the frequency is routed through the repeater – like a mobile phone tower. You will need an individual repeater per channel you want boosted. They can be used inside a building where the signal needs to penetrate many layers or outside to extend the range where topographical interference occurs at ground level or further distances are required.